Among the various security automation tools available, SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response) and SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) stand out as two vital tools that can help organizations automate some of the most time-sensitive security tasks.
SIEM focuses on data collection and analysis, providing insights into potential security issues, while SOAR automates response actions and orchestrates workflows to manage incidents effectively.
In this blog post, we're exploring how these essential tools work, the functions they cover, and how you can choose the right security automation tool for your organization.
Overview of Security Automation Tools
Security automation tools began to emerge in the early 2000s as the volume and complexity of cyber threats grew beyond the capacity of manual security processes. Initially designed to automate simple, repetitive tasks, these tools have since advanced to handle more sophisticated functions, integrating with various security technologies to streamline and enhance security operations.
Today security automation tools have become indispensable in modern cybersecurity, providing essential support to security teams and enhancing overall security posture. On average, organizations that extensively implement security AI and automation save USD 1.76 million more than those that do not.
Key functions of Security Automation Tools
Security automation tools encompass a broad spectrum of functions, including:
- Incident Response: Automating responses to detected threats to mitigate damage quickly.
- Threat Intelligence: Collecting and analyzing threat data to provide actionable insights.
- Vulnerability Management: Scanning and identifying vulnerabilities within systems.
- Compliance Management: Ensuring adherence to regulatory standards and policies.
Security automation tools alleviate the burden on security teams by automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks, allowing professionals to focus on strategic activities like threat hunting and incident analysis. By reducing manual workload, these tools enhance efficiency, improve response times, and increase accuracy. Automating processes also eliminates human errors and ensures consistency in results.
Understanding SIEM
Gartner defines SIEM as "the market for the customer's need to analyze event data in real-time for early detection of targeted attacks and data breaches, and to collect, store, investigate, and report on log data for incident response, forensics, and regulatory compliance." Essentially, SIEM technology centralizes and analyzes event data from various security devices, network infrastructure, systems, and applications. While it primarily relies on log data, it also processes other data types like network telemetry. This data, when combined with contextual information about users, assets, threats, and vulnerabilities, is normalized to facilitate comprehensive analysis for security monitoring, user activity tracking, and compliance reporting. SIEM excels in providing real-time event analysis for security monitoring and also offers long-term analytics for historical data.
Advantages and Limitations of SIEM
SIEM offers several key benefits:
Early Threat Detection: By analyzing event data in real-time, SIEM helps identify potential security threats and breaches early.
Comprehensive Data Aggregation: Collects and correlates data from various sources, providing a holistic view of the security landscape.
Regulatory Compliance: Supports compliance efforts by generating detailed reports required by various regulatory standards.
Contextual Analysis: Enhances the accuracy and relevance of its analysis by combining event data with contextual information.
Despite its advantages, SIEM also has some limitations:
Manual Intervention: Often requires significant human intervention to investigate and respond to incidents.
Scalability Issues: For large organizations with extensive data, SIEM can become resource-intensive and may require substantial infrastructure.
False Positives: Can generate a high number of false positives, which can overwhelm security teams and reduce the efficiency of threat detection.
Understanding SOAR
Gartner defines SOAR as technologies that enable organizations to collect inputs monitored by the security operations team, such as alerts from SIEM systems and other security technologies.
These inputs are utilized for incident analysis and triage, leveraging both human expertise and machine capabilities. SOAR aids in defining, prioritizing, and standardizing incident response activities. It enables organizations to develop incident analysis and response procedures in a digital workflow format.
Advantages and Limitations of SOAR
SOAR offers several key benefits:
- Automation of Repetitive Tasks: Automates low-level, time-consuming tasks such as opening and closing support tickets, event enrichment, and alert prioritization.
- Enhanced Efficiency: By automating repetitive processes, SOAR frees up security analysts to focus on more strategic tasks, improving overall efficiency.
- Standardized Workflows: Allows for the creation of digital workflows that standardize incident response procedures, ensuring consistent and efficient responses.
- Integration Capabilities: Can trigger automated actions in integrated security tools, enabling complex security operations to be carried out seamlessly.
- Improved Response Time: Reduces the mean time to resolution (MTTR) by streamlining and automating incident response activities.
SOAR also comes with some limitations:
S
- Dependency on Accurate Data: The effectiveness of SOAR depends heavily on the quality and accuracy of the data it processes. Poor data quality can lead to ineffective responses.
- Maintenance and Updates: Requires regular updates and maintenance to ensure compatibility with evolving security tools and threat landscapes.
- Learning Curve: Security teams may need extensive training to effectively utilize SOAR tools and maximize their benefits.
- Complex Setup: Implementing SOAR solutions can be complex and may require significant initial configuration and ongoing management.
SIEM vs SOAR: Key Differences
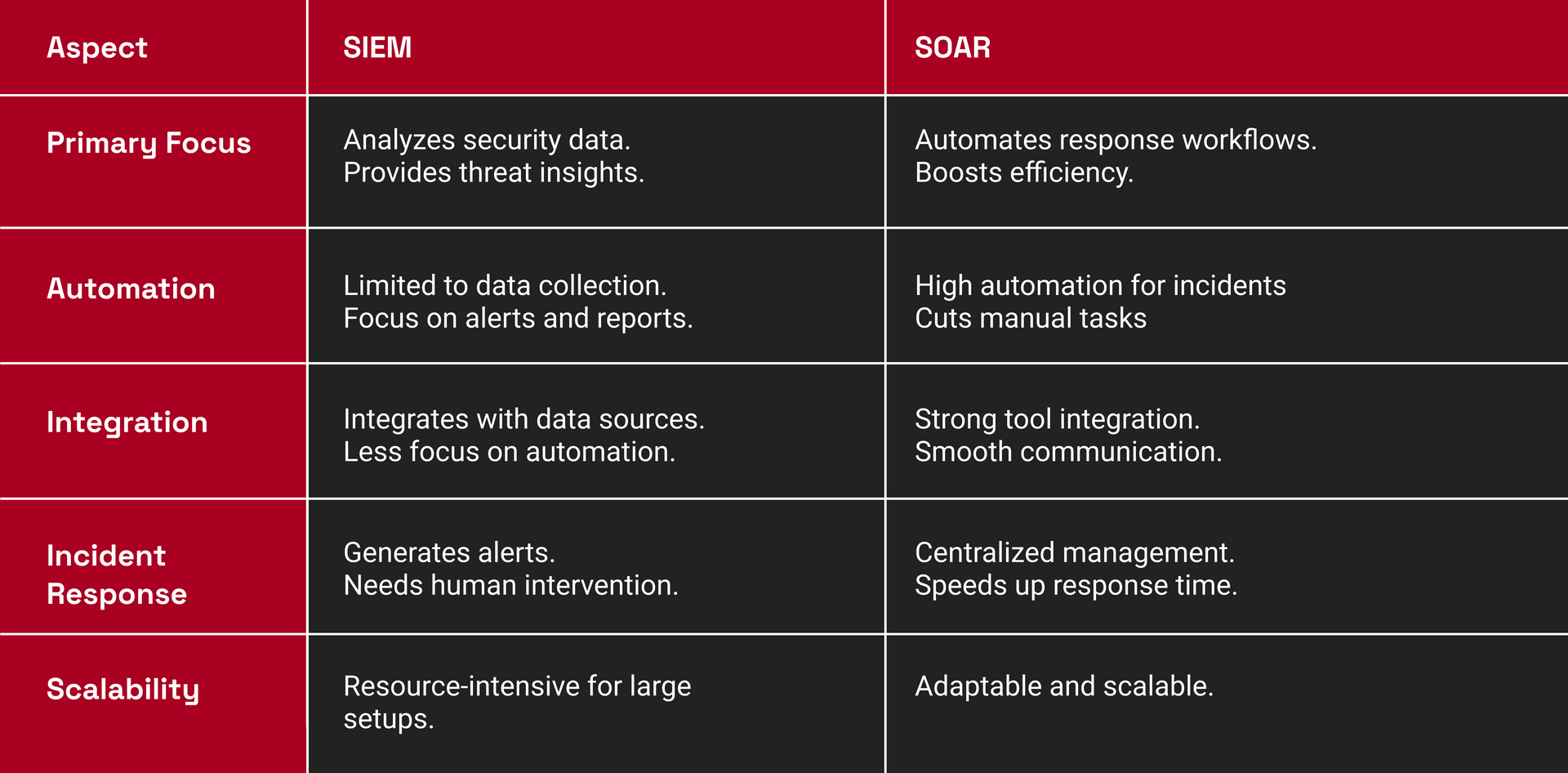
Do You Need Both SIEM and SOAR?
Organizations benefit from using both SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) and SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response) because each serves distinct but complementary functions. SIEM excels in real-time event monitoring and threat detection by analyzing log data from various sources, providing critical alerts. However, it lacks the automated response capabilities that SOAR offers. SOAR enhances the security process by automating the validation of alerts, orchestrating incident responses, and reducing manual intervention. This combination allows for efficient threat detection and swift, automated responses, creating a strong and complete security solution.
SIEM + SOAR and Much More
Wouldn't it be great if you could have all the functions of a SIEM and SOAR in one tool? The Evolve suite of products delivers exactly that, combining the advanced analytics and real-time monitoring capabilities of SIEM with the automated incident response and orchestration power of SOAR.
Check out how our XDR compares to other SIEMs:
| Capability | General SIEM Solutions | EvolveXDR |
|---|---|---|
| Security Analytics | Aggregates event data | Collects, aggregates, indexes, and analyzes security data for intrusions, threats, and anomalies |
| Real-time Monitoring | Limited capabilities | Real-time monitoring and security analysis for fast threat detection and remediation |
| Intrusion Detection | Basic log analysis | Detects malware, rootkits, and anomalies through agents and signature-based analysis |
| Log Data Analytics | Analyzes and stores data | Reads OS and application logs, forwards them securely for rule-based analysis and storage |
| File Integrity Monitoring | Limited scope | Monitors file changes, permissions, ownership, attributes, and integrates with threat intelligence |
| Configuration Assessment | Basic log-based detection | Correlates software inventory with CVE databases for automated vulnerability assessment |
| Incident Response | Basic monitoring | Monitors and assesses system/application configurations against policies, with customizable checks |
| Regulatory Compliance | Compliance reporting | Helps meet industry standards like PCI DSS, GDPR, NIST, SOC2, and HIPAA through comprehensive controls |
| Cloud Security Monitoring | Limited cloud integration | Monitors cloud infrastructure at API and instance levels, integrates with AWS, Azure, Google Cloud |
| Containers Security | Basic monitoring | Monitors Docker hosts and containers, detects threats, vulnerabilities, and anomalies in real-time |
But it doesn't stop there—Evolve also offers penetration testing, DNS sinkholing, application security testing, leaked password monitoring, cyber threat intelligence, and dark web monitoring. With Evolve, you get a comprehensive, all-in-one solution that enhances your security posture and simplifies your operations.
The Future of SIEM and SOAR: A New Era with AI
The cybersecurity landscape is changing fast, and the future of SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) and SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response) systems is set to be driven by AI and machine learning (ML). These technologies are transforming how security teams detect, respond to, and manage threats, offering smarter, more efficient ways to protect against today’s complex cyber risks.
AI-driven SIEM systems are already making a big impact by helping organizations improve threat detection and response times. With the ability to analyze large volumes of data in real time, AI can spot patterns and potential risks faster than traditional methods. This means security teams can act more quickly and effectively, reducing the time spent sifting through alerts and identifying the most pressing threats. The use of predictive analytics in SIEM also helps organizations stay ahead of emerging threats, making their defenses more proactive.
On the other hand, SOAR solutions are evolving to simplify the management of complex security environments. These platforms integrate various security tools, automate routine tasks, and ensure a faster, more coordinated response during incidents. When combined with AI/ML, SOAR systems can significantly enhance a team’s ability to manage incidents. AI acts as a powerful force multiplier, allowing security analysts to focus on higher-level tasks while automating the repetitive work that can often slow them down.
Despite the clear benefits, there are still challenges to overcome. Data quality, system complexity, and the cost of implementation are just a few of the hurdles organizations face. There's also a shortage of skilled professionals who can manage and optimize these advanced systems. But as organizations begin to integrate AI more deeply into their cybersecurity strategies, these barriers will likely become less daunting.
Looking ahead, we can expect the lines between SIEM and SOAR to blur even further, with AI playing a central role in both. The next generation of these systems will not just automate tasks—they will enhance decision-making, provide deeper insights, and help security teams respond more effectively to the evolving threat landscape.
How AI is Enhancing Threat Detection and Reducing False Positives in SIEM Systems
AI is fundamentally transforming how SIEM systems handle threat detection, addressing one of the most persistent challenges: false positives. Modern platforms leverage machine learning (ML) to better differentiate between legitimate threats and benign activities. For instance, ML algorithms analyze historical patterns to prioritize alerts that align with past malicious incidents while reducing the priority of those that resemble previous false positives. This not only reduces noise but ensures that analysts focus their attention on critical threats. Additionally, advanced tools like MADE (Malicious Activity Detection in Enterprises) apply supervised ML to detect malicious communications within enterprise networks, achieving high precision with minimal false alarms. AI also powers innovations like dynamic case assignment and queue prioritization, ensuring that the right analysts handle the most urgent cases, boosting overall SOC efficiency. With AI continually learning from evolving threat patterns, SIEM systems are now more effective than ever at minimizing distractions and enhancing security operations.
The Role of Natural Language Processing in Streamlining SOAR Operations
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is proving instrumental in optimizing SOAR operations by automating the extraction and analysis of threat intelligence (CTI) from unstructured sources like blogs, forums, and tweets. Tools leveraging NLP generate structured Indicator of Compromise (IOC) files, reducing manual effort and enabling faster, more accurate configuration of security tools. Advanced systems go further by using supervised machine learning to identify high-level attack patterns and techniques, streamlining the SOC analysis process and enhancing overall threat response efficiency.
Get a Consultation for Your Business Today
Contact us today for a personalized consultation to discover how the Evolve suite of products can meet your specific security needs. Our team will work with you to assess your current security posture, identify potential vulnerabilities, and tailor a solution that maximizes protection and efficiency.
Schedule a consultation with one of our experts today!
Sources:
Kinyua, J., & Awuah, L. (2021). AI/ML in Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response: Future Research Directions. College of Information Sciences and Technology, Pennsylvania State University, and University of Maryland Global Campus.
Vinay Dutt Jangampet, The Rise of The Machines: AI-Driven SIEM User Experience for Enhanced Decision-Making, International Journal of Computer Engineering and Technology 12(3), 2021, pp. 74-83.






