As more and more sophisticated crime operations spread across the globe, and as new software vulnerabilities are discovered and exploited by cyber criminals, companies have an increasing obligation to assign experts and analysts to systematically identify and remediate threats. One invaluable tool for creating and implementing an effective security program is a detailed and comprehensive Threat and Risk Assessment (TRA).
What is a Threat and Risk Assessment?
A TRA is a process used to identify, assess, and remediate risk areas. The result of this process will be to, hopefully, harden the network and help prevent (or at least reduce)
cyber attacks.
Threat and Risk Assessment provides a more thorough assessment of security risk than the standard assessments, such as studying threat statistics or conducting a facility walk-through. Using information and data from various methods, security professionals combine these pieces to create a comprehensive plan for effective security management while assessing a company’s compliance with industry practices and applicable laws.
The Goals of Threat and Risk Assessment
The main objective of Threat and Risk Assessment is to protect organizations against liabilities by identifying and understanding the various risks facing the client property and community. Threat and Risk Assessment identifies exposures by determining potential security weaknesses and taking the appropriate actions to reduce the impact of threatening events and manage the risks.
An effective risk assessment helps organizations understand and prioritize potential threats by evaluating the impact of risks. Here's a brief risk assessment template for reference:
Assessment Type:
- Tier 1: High Risk (Significant business exposure)
- Tier 2: Medium Risk (Moderate impact)
- Tier 3: Low Risk (Minimal impact)
Inherent Risk:
The risk present without any cybersecurity defenses.
- Key Questions:
- What’s the worst that could happen?
- How serious would a potential incident be?
Residual Risk:
The risk that remains after security measures have been applied.
- Key Questions:
- What risks are still active with current defenses?
- What types of incidents are still possible?
When do you need to assess the risk of insider threats?
Not only does the TRA assess external threats, but it can also be effective in assessing and protecting from internal threats. If you are an organization that works with sensitive data, you should also assess the risk of insider threats. No one wants to imagine that their employees can be a security risk, but an estimate of
63% of cyber attacks are internal. There are three steps to assess the risk of insider threats:
- Audit your organization’s cybersecurity;
- Apply for cybersecurity insurance;
- Comply with laws, regulations, and security standards.
Audit your organization’s cybersecurity
Risk assessment is an essential part of risk management strategy. aside from being part of a regular routine, here are just a few of the times when your organization should perform an assessment:
- To plan for reorganisation or expansion of a business;
- An abnormally high increase in cybersecurity incidents within your industry;
- A known attack on your organization.
Apply for cybersecurity insurance
Just as we insure our buildings and businesses for risks such as fire, theft, and natural disasters, it’s advisable to also insure your company for cyber attacks. As with most insurance, the insurance company may require an assessment before issuing the policy, and in order to help define the terms of your coverage. The risk assessment method used by insurers for analyzing an organization’s risk level includes:
- Client meetings;
- Research;
- Underwriting questionnaires;
- Risk audits;
- Open-source intelligence;
- Threat intelligence;
- Third-party assurance reports.
Comply with laws, regulations, and security standards
There are many laws and regulations that directly involve the security of data. Whether it is dealing with
PCI,
HIPAA, or organisations such as
ISO and
NIST, assessing the risk of insider threats is mandatory. Below, we will run through a few of these regulatory requirements:
NIST Risk Assessment Guide
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), suggests the following steps:
- Prepare for the assessment
- Here you define the scope and purpose of the assessment, as well as constraints (you may, for example, limit the assessment to only the customer-facing network). Further, it explains the risk model you are comfortable with, sources of information, and which analytical approaches you will use.
- Conduct the assessment
- At this stage, you identify the relevant sources of threats and events, together with any vulnerabilities that could be exploited. Further, you determine the potential and likely impact of the specific threat events.
- Share and communicate risk assessment information
- To support risk responses, communicate risk assessment results to decision-makers and other relevant personnel.
- Maintain the risk assessment
- This includes remediating vulnerabilities (such as updating and patching software, or monitoring known, but low-level risks (using an IDS).
PCI DSS Risk Assessment Guide
The PCI Guide offers pages of guidelines and assessment values to consider. Here are just a few of the most important tips:
- All data should be encrypted, both in-transit and at-rest;
- Monitor and assess networks on a regular basis;
- Only store customer data when necessary (for example, keeping a card on file at popular retail websites).
Guidance on Risk Analysis Requirements under HIPAA
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) requires that health organisations conduct a regular risk assessment. During this assessment, auditors should check for:
- Malicious software installation;
- Computer- and network-based attacks;
- Inaccurate data entry;
- Unauthorised access to electronically protected health information.
Engaging Stakeholders in Risk Assessments
In the context of cybersecurity risk mitigation, involving a diverse range of stakeholders is essential for a comprehensive threat and risk assessment. These stakeholders, including board members, executives, managers, employees, IT teams, customers, and external entities like suppliers and regulators, bring unique perspectives crucial for effective risk management. The process begins with identifying and categorizing stakeholders, followed by transparent communication of the risk strategy. Actively involving stakeholders in risk assessment, consulting them on treatment plans, and collaborating on implementation ensures a collective and informed approach. Regular updates on risk monitoring maintain transparency and foster a culture of cybersecurity awareness. To enhance stakeholder engagement, consider tailoring communication methods, addressing concerns promptly, and promoting a pervasive cybersecurity mindset across the organization.
INTEGRATING NEW TECH IN RISK ASSESSMENT
When introducing new technology for safety risk assessments, it is important to remember that it is meant to complement and enhance existing practices, not replace them. The first step is to clearly define the goals you want to achieve with the technology. Next, choose the technology that best fits your needs. It is crucial to seamlessly integrate this technology into your current workflow. Ensure that everyone understands their role in using the technology and handle the data it produces responsibly. Once the technology is operational, regularly evaluate its performance and make any necessary adjustments and improvements. However, it is essential to remember the core principles: always act ethically and legally, and prioritize stakeholder privacy and rights.
CONTINUOUS MONITORING IN RISK ASSESSMENT
The evolving nature of cyber threats necessitates a transition from periodic assessments to
continuous monitoring. Continuous monitoring involves real-time tracking of security metrics, network activities, and potential vulnerabilities. It enables you to oversee high-risk assets and systems and promptly respond when needed. The good news is that continuous monitoring can be automated, ensuring the quality of assessments without overwhelming your team.
Five Key Steps for Assessing Insider Threats
As we mentioned at the beginning of this article, while external threats are certainly a risk, a large number of attacks come from internal sources. Insider threats pose a significant risk to organizations, as they involve malicious or negligent actions from employees, contractors, or other insiders who have authorized access to sensitive information, systems, or assets.
An insider threat can cause significant damage to an organization, ranging from physical damage to intellectual property, financial loss, and reputation, ultimately resulting in reduced profitability and competitive advantage.
For this reason, it is vital to assess your organization’s security from the inside, as well. A threat and risk assessment program can help you to identify and address insider threats, thus reducing the overall risk to your organization and improving the effectiveness of your information security program.
A typical insider threat and risk assessment would look like this:
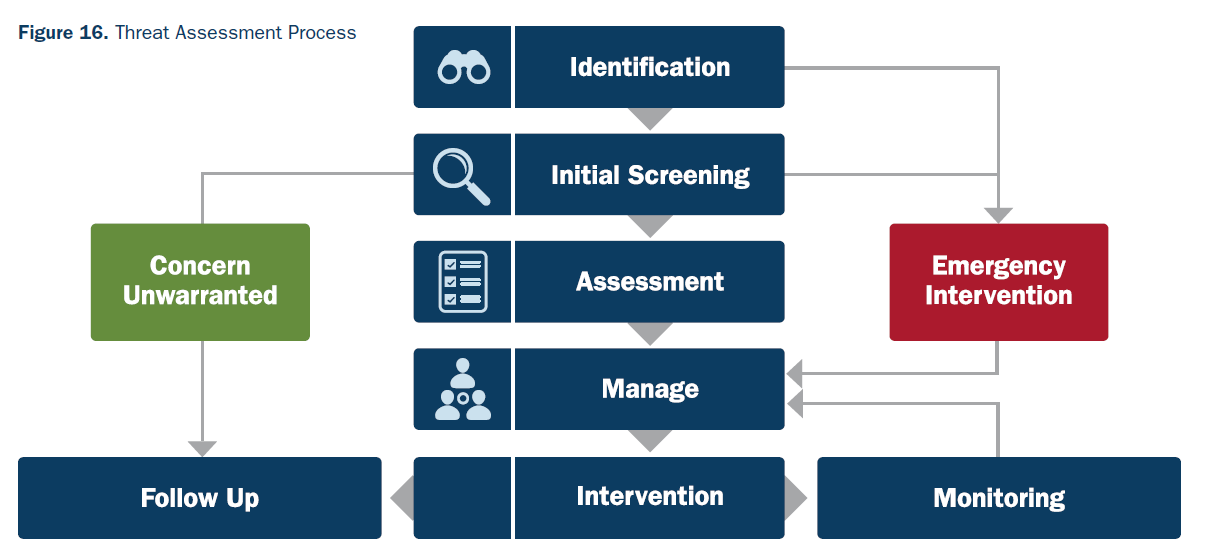
Source: CISA
We've broken down the threat assessment process into five key steps. Keep reading to learn more.
IDENTIFYING ESSENTIAL ASSETS OF AN ORGANIZATION
Risk assessment starts by distinguishing the valuable assets that insiders can compromise in an organization. It would help if you, therefore, focused on:
- Access to admin accounts and servers (both physical and cloud);
- Confidential information, such as trade secrets;
- Employee’s sensitive data;
- Subcontractors’ and partners’ data;
- Crucial services and systems.
In this step, you need to identify the assets and data that need to be protected, and determine the potential insider threats that could compromise them and the current level of exposure of your critical assets to insider threats. You also need to define the goals and objectives of the assessment, such as identifying vulnerabilities and weaknesses, assessing the effectiveness of existing controls, and developing mitigation strategies.
A penetration test can help you determine if your current security controls are effective to protect these assets. Additionally, it can help to uncover any vulnerabilities that may be exploited by an insider.
Defining the possible insider threats
Activities done by legitimate users but with negative connotations are referred to as insider threats. These include:
- Sensitive data disclosure;
- Misusing, changing, or deleting data;
- Malware uploads (both intentional and unintentional);
- Failure to follow the principles of least privilege.
Insider threats can take many forms. According to CISA, these are the main types of insider threats:
- Unintentional Threats: Unintentional threats include negligent employees that could expose your organization to threats, and accidents or mistakes that cause unintended risks to your organization's data;
- Intentional Threats: Intentional threats are malicious actions taken by an insider with the intention of harming your organization's data or systems. This can include employees who are disgruntled or who are working against the organization due to monetary or other personal reasons;
- Other Threats: Threats such as third-party and vendor access to your organization's systems and data, and insiders who collaborate with outside parties can also pose a risk to your organization's data and systems.
All these threats can manifest in your organization in different ways. According to CISA, these 'expressions' of insider threats can include workplace violence, terrorism, sabotage, and espionage. Here's a chart by that illustrates the various expressions of these insider threats.
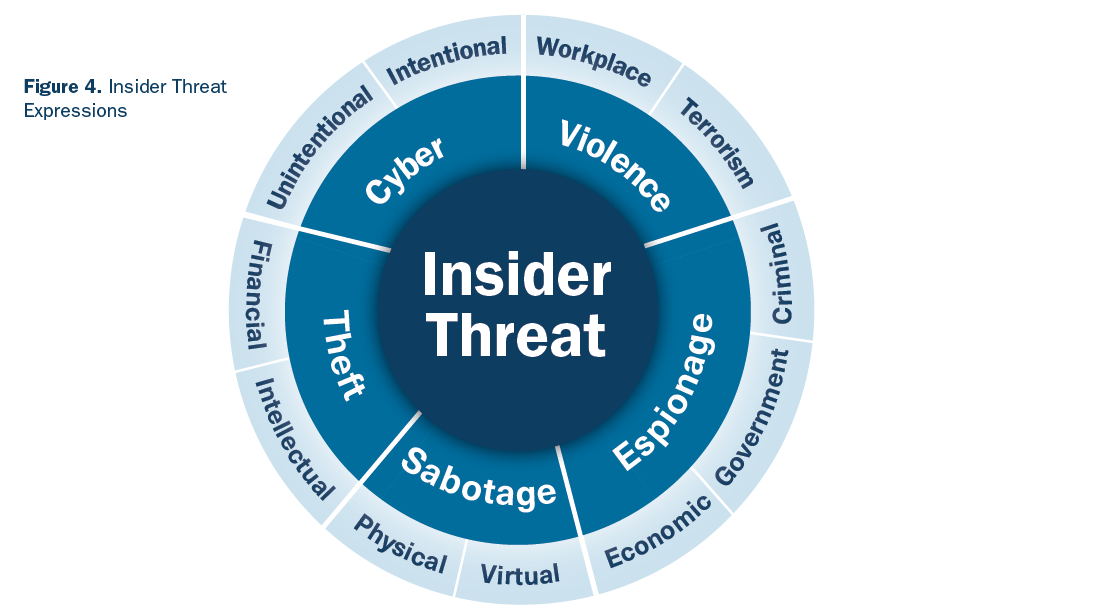
Source: CISA
To identify potential insider threats, you need to review access logs, conduct employee interviews, and analyze past incidents. It's also important to keep an eye out for suspicious activity, or concerning behaviors in your employees that may include any of the abovementioned expressions of insider threats. This will help you identify individuals who have authorized access to your organization's systems and data, and who may pose a risk to the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of that data.
PRIORITIZE RISKS
Once you've identified potential insider threats, it's time to classify and prioritize them, based on the level of risk they pose to your organization.
Here, you determine which risks most threaten your business, both in terms of profitability and customer confidence. A risk matrix can help you determine the level of each risk. Here are the four factors that you should analyze:
- How critical the threat is;
- Importance of the at-risk assets;
- Likelihood of an occurrence;
- System vulnerability.
While evaluating the risk of possible insider threats, it is important to consider the following:
- Does the insider have an interest or motive in harming the organization?
- If yes, do they have the capability to carry out their plan?
- What could be the extent of the damage if the insider were to act?
- Is there evidence of the insider's intentions?
CREATE A RISK ASSESSMENT REPORT
Wrap your risk assessment results into a comprehensive report. This will help to simplify the decision-making processes at the further stages of the management strategy. The report can help you to:
- Communicate results of risk assessment to decision-makers;
- Share the risk-related information with your employees;
- Adjust your risk management approach (updating software more regularly, making password requirements more stringent, etc.).
As per CISA's Insider Threat Mitigation Guide, the ultimate question to answer in a threat assessment is if the insider is on a path to cause harm. And if they are, how far along are they? And when can you intervene?
MAKE INSIDER RISK ASSESSMENT A COMMON PRACTICE
You should note that with time, organisations tend to change either software and tools, or expand their departments and their practices. Such changes create new vulnerabilities, and your organization should therefore conduct a risk assessment regularly.
Also remember that the threat assessment is not a one-time event and is a process that requires continuous monitoring and updating. If your initial assessments and strategies fail, revisit your threat assessment to find out why and refine your approach accordingly.
Conclusion
Risk assessments collect essential information and expose weak cybersecurity spots. They also provide an organization with the tools they need to evaluate the consequences of potential security incidents. Lastly, they also help an organisation improve its security practices, helping to prevent incidents in the future. While it is impossible to prevent all incidents, risk assessments are a vital tool for protecting any organization from the ever-growing threat of cyber criminals.









